Graphic maps are images that can impart certain properties to a material.
These include fine surface details, gloss, luminous sources, light penetration, and much more.
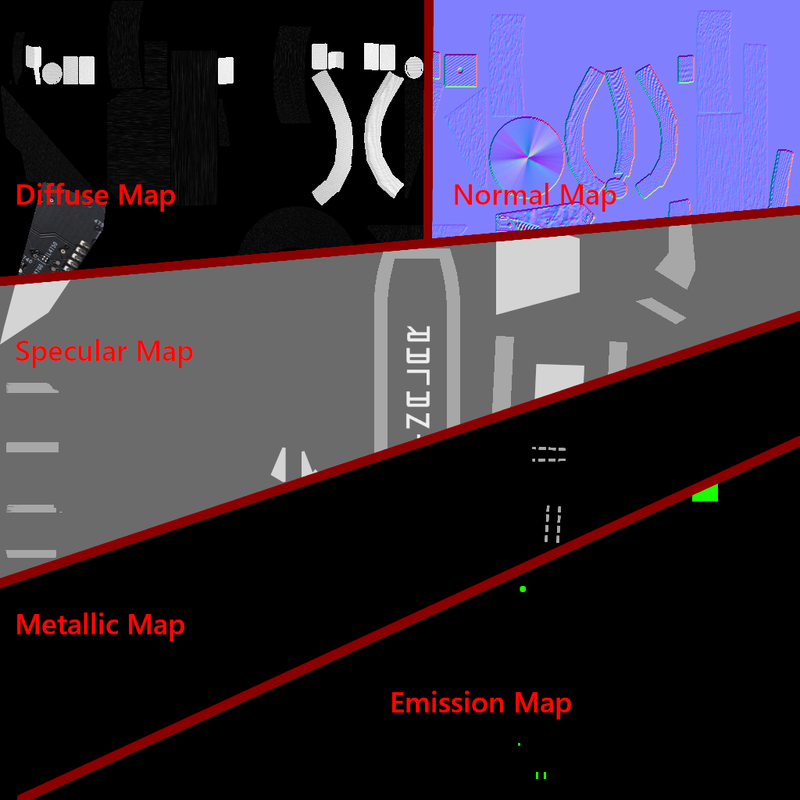
Here you can see the maps for one and the same material:
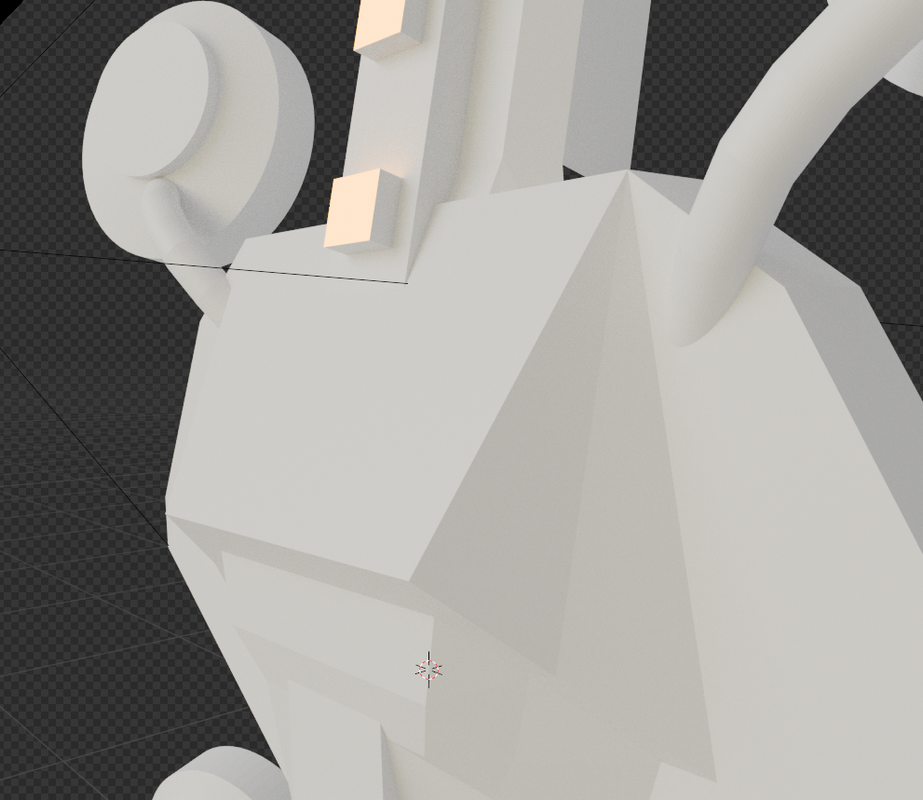
Without these maps, a 3D model is colorless, contrastless and empty:
Diffuse Map:
Diffuse maps are, so to speak, the base material, the visible color surface of a 3D model:
The diffuse map alone gives the model a coat of paint. It looks quite good, but it appears flat and lacks contrast.
Normal Map:
To improve the surface's appearance, the normal map comes into play.
It can be thought of as the elevation information on a map.
The normal map is used to calculate shadows, even though there's actually nothing on the surface of the 3D model that could cast a shadow.
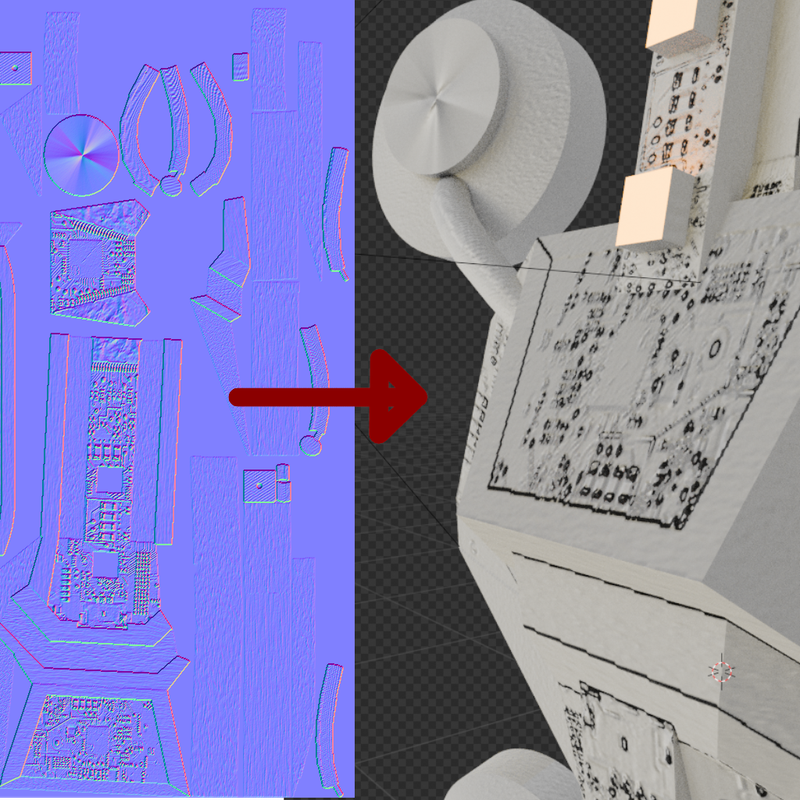
This makes a 3D model appear much more contrasty.
Specular Map:
This graphic shows where the 3D model should reflect and how much.
Metal Map:
This graphic indicates where the 3D model should have a metallic appearance. This includes, for example, a metallic sheen. In this example, the solder joints of the SMD resistors should have a metallic appearance:
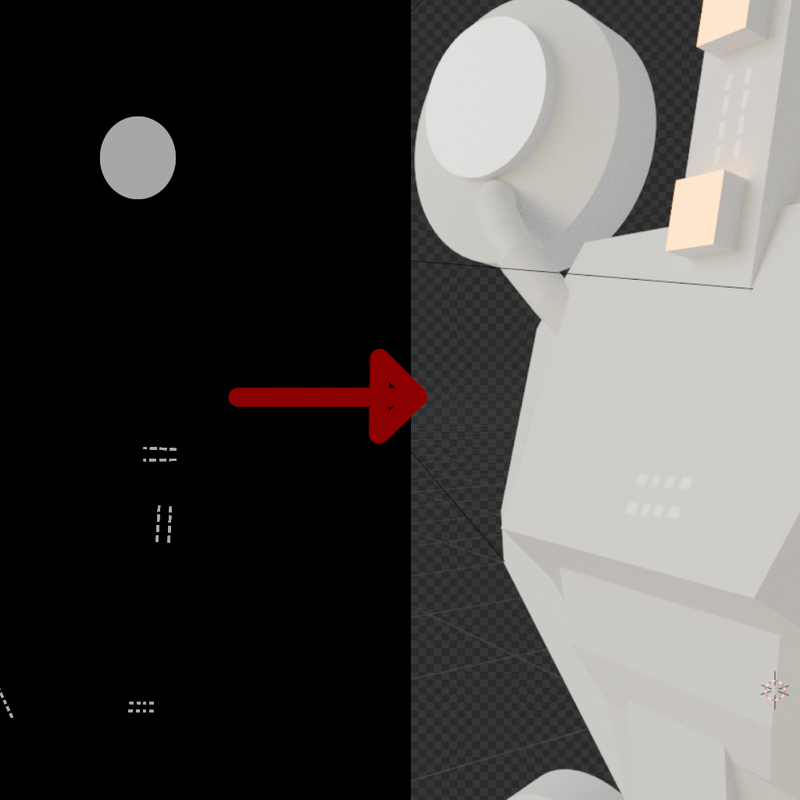
Emission Map:
This map specifies where the texture should glow. Shown here in green.
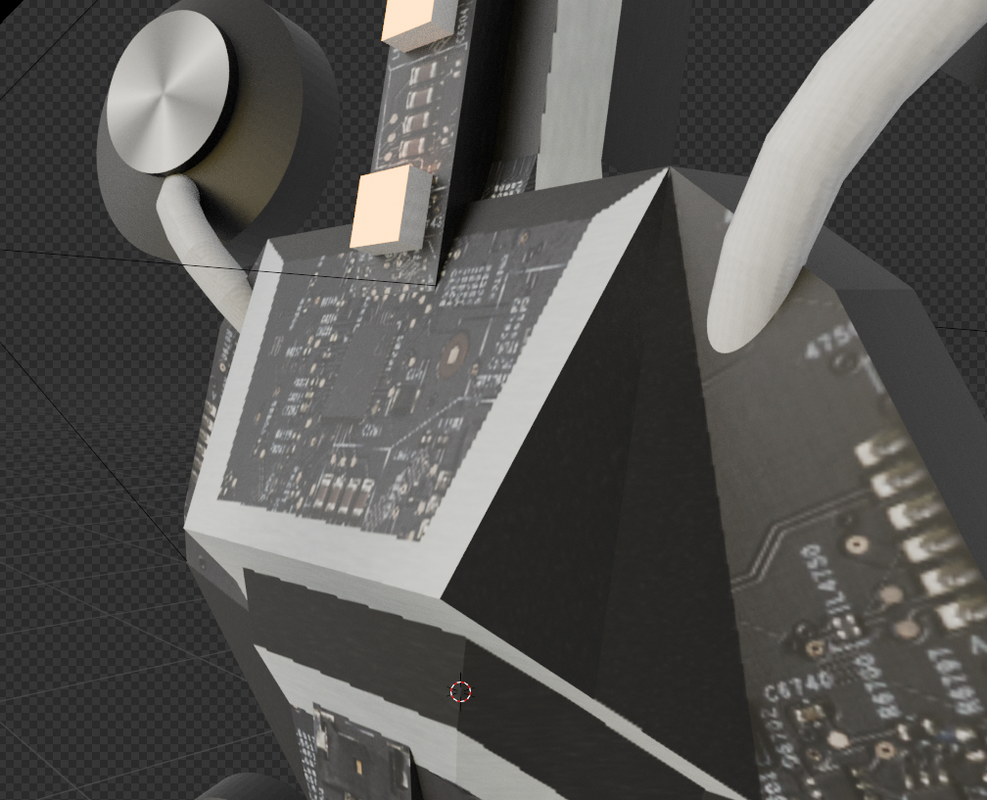
The result of all this looks like this:
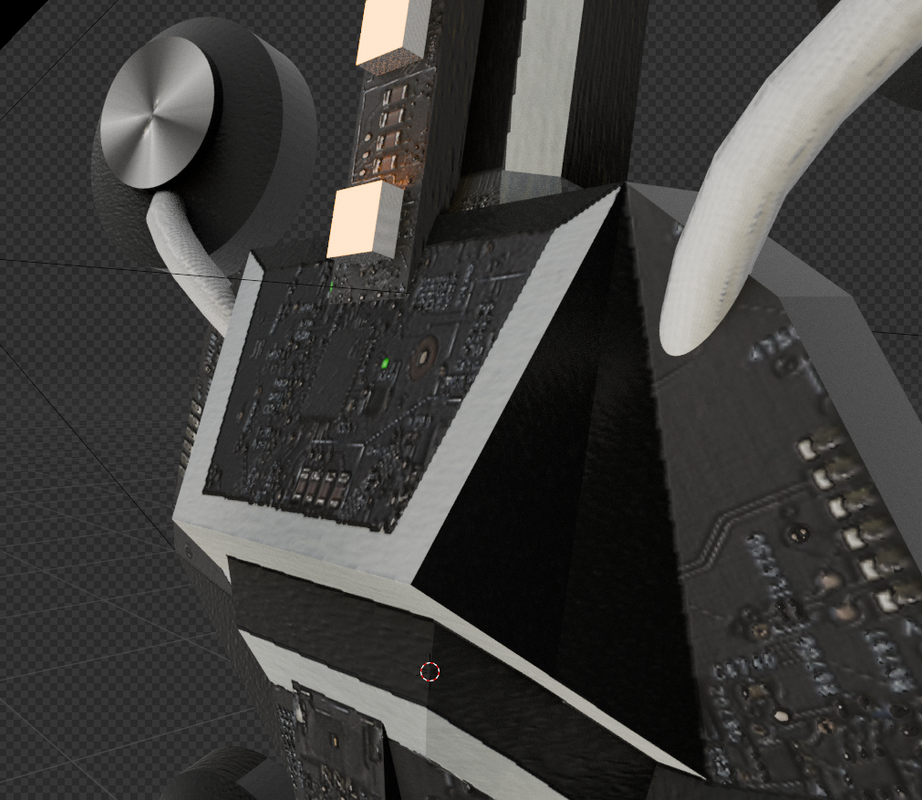
Of course, you can see the diffuse map, and you can clearly see the normal and emission maps.
Metal and specular maps are clearly visible in changing lighting conditions.
These techniques are used in most 3D games and other graphics applications.










2 comments